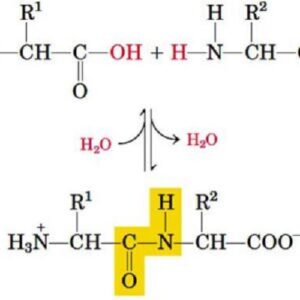
Description
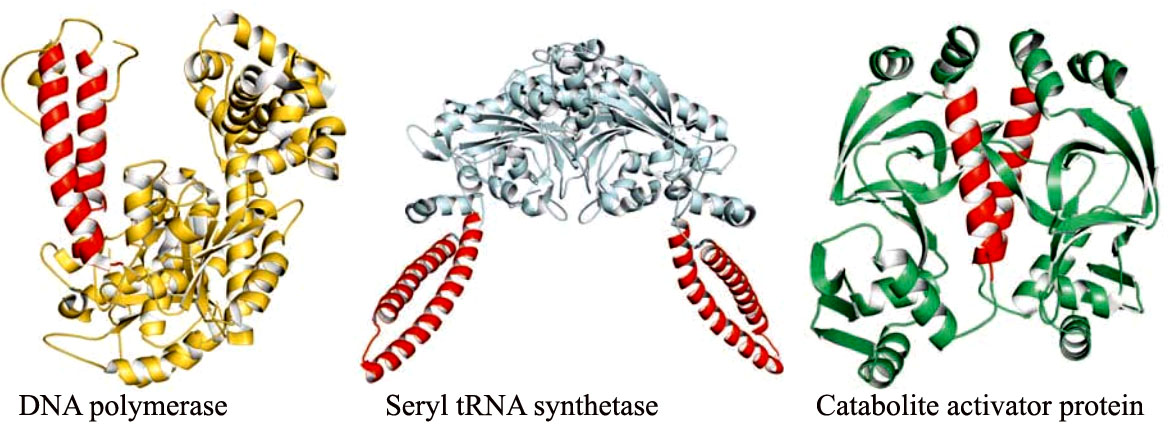
Tertiary structure refers to the complete three-dimensional structure of the polypeptide units of a given protein.
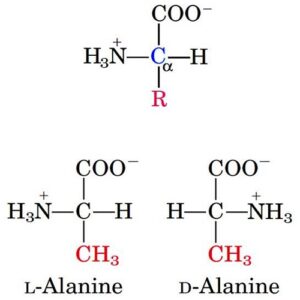
- Tertiary structure is formed due to interactions between side chain R group of amino acid residues present in the proteins.
- Nearly all of the polar, hydrophilic R groups are located in the surface, where they may interact with water

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.