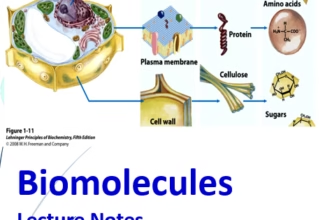
RNA: Types, Structures, Properties and functions
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
- RNA is much more abundant than DNA
- Various types of RNA are existed in the cells
- They are involved in gene expression and regulation
- RNA may be the genetic material in some of the virus
- They unstable in alkali undergo hydrolysis
- Mostly single stranded
- Present in both cytoplasm and nucleus
Difference between RNA and DNA
| RNA | DNA |
| Presence of Ribose | 2’ Deoxyribose sugar |
| Composed of A, G, Uracil and Cytosine | Composed of A, G, Thymine and Cytosine |
| Mostly single stranded | Double stranded |
| Intra-strand H-bonding | Inter strand H-bonding |
| RNA is composed of 100-5000 np | Large made up of millions of np |
| Hydrolysis by alkali | Alkali resistant but get denatured |
| Involved in gene expression and regulation in cell | Storage of genetic information |
Types of RNA
| Types of RNAs | Primary Function(s) |
| mRNA – messenger | translation (protein synthesis) , Regulation |
| rRNA – ribosomal | translation (protein synthesis) (Enzymatic function) |
| t-RNA – transfer | translation (protein synthesis) |
| hnRNA – heterogeneous nuclear | precursors & intermediates of mature mRNAs & other RNAs |
| scRNA – small cytoplasmic | signal recognition particle (SRP) tRNA processing (Enzymatic function) |
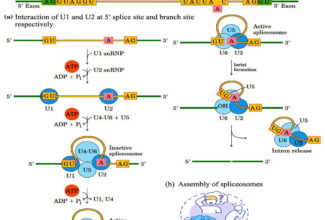
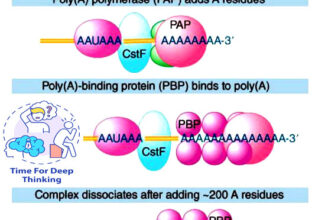
| snRNA – small nuclear snoRNA – small nucleolar | mRNA processing, poly A addition (Enzymatic function) rRNA processing/maturation/methylation |
| regulatory RNAs (siRNA, miRNA) | regulation of transcription and translation, other?? |