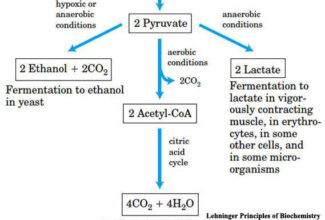
Linkage Recombination and chromosome mapping
Linkage Recombination and chromosome mapping
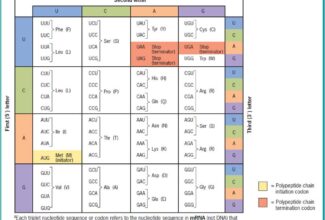
Linkage
Morgan’s concept of Linkage
- Morgan (1910) while working on Drossophila stated that coupling and repulsion are two aspects of the same phenomenon, which is described as linkage. He defined linkage the tendency of the genes, as present in the same chromosome, to remain in their original combination and to enter together in the same gamete. Morgan and Castle formulated the chromosomal theory of linkage. It has following characteristics:
- Genes that show linkage are situated in the same chromosome.
- Genes are arranged in linear fashion in the chromosome i.e., linkage of genes is linear.
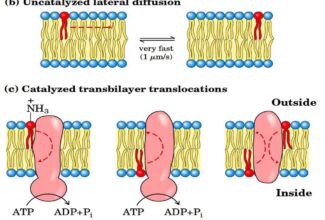
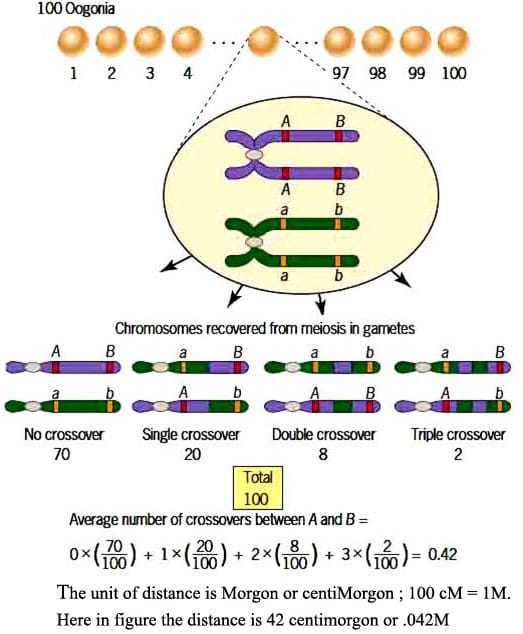
- The distance between the linked genes is inversely proportional to the strength of linkage. The genes which are closely located show strong linkage, where as those which are widely separated have more chances to get separated by crossing over.
- Linked genes remain in their original combination during course of inheritance.
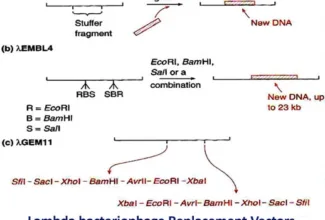
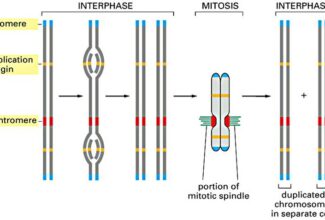
The chromosomal theory of linkage is widely supported from the cytological studies. It has helped in the construction of linkage maps of chromosomes (the distance between the genes is determined by the percentage of cross overs).