Bacterial Plasmids Properties and Types
Bacterial plasmids: Types of plasmids, Compatibility and incompatibility, Mobilizable plasmids, Copy number of plasmids, Fertility inhibition, Donation and conduction
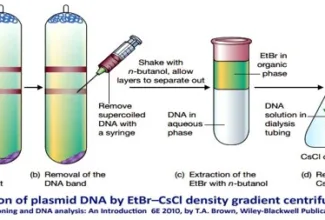
- Plasmids are extra chromosomal, covalently closed circular, stably inherited, autonomously replicating DNA molecule present in bacteria and in some lower eukaryotes.
- Plasmids are not required for bacterial growth however, confer additional advantage to bacteria in a particular environment.
- The plasmids are small in size generally 0.2-4% of the bacterial chromosome and their replication depends upon host metabolic machinery
Properties of plasmids
- Autonomous replication
- Plasmids possess origin of replication which enable them to multiply independently.
- The smaller plasmids use replication machinery of host for replication while larger plasmids code specific enzyme necessary for their replication in addition to host replication machinery.
- Some plasmid replicate by inserting themselves into the bacteria chromosome.
- These integrative plasmids (episomes) are stably maintained in this form through cell divisions but can also have abilty exist as independent elements.
- Size and copy number
- Plasmid size ranges from 1.0 kb for the smallest to over 250 kb for largest plasmids.
Plasmid Size Organism
ColE1 6.4 Pseudomonas and other E.coli
F 95 E.coli
TOL 117 Pseudomonas putida