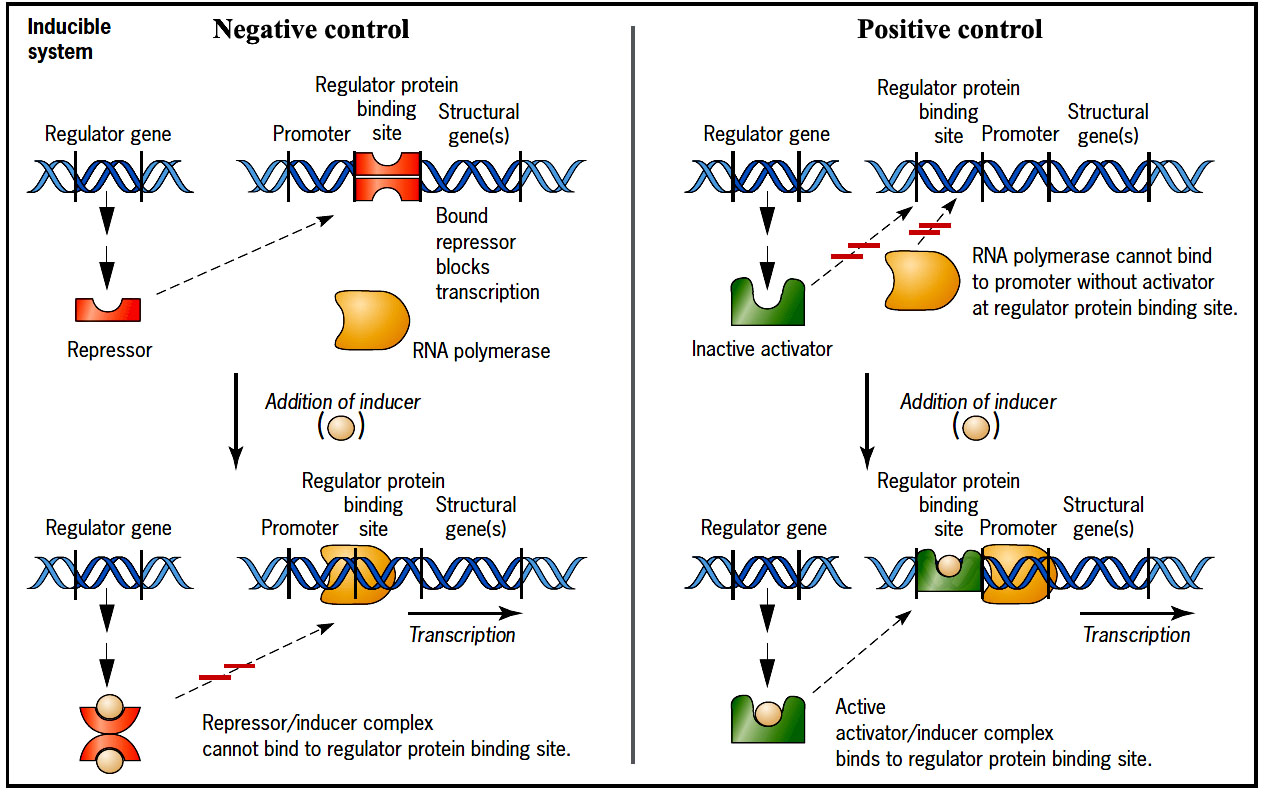
Regulation of Prokaryotic gene expression
Regulation of Prokaryotic gene expression
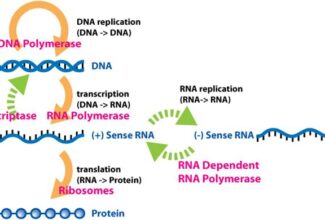
Gene expression in bacteria is highly influenced by changing environment. Gene expression is regulated at several levels in bacteria:
- Transcription
- mRNA processing
- mRNA turnover
- Translation
- Post translational modification










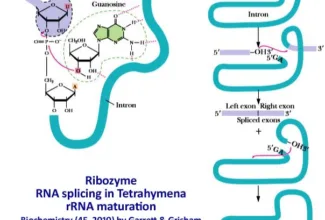
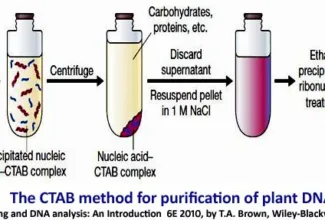
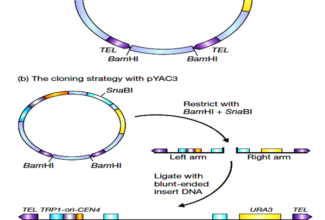


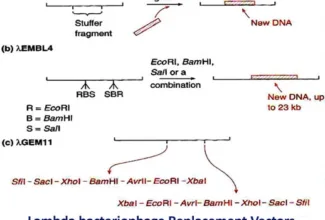
























































































































Nice