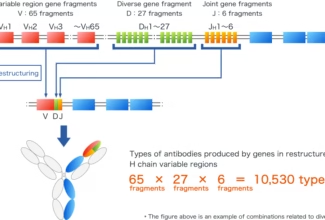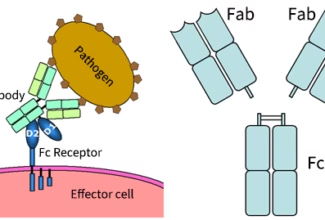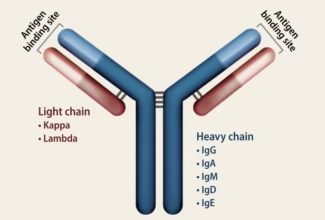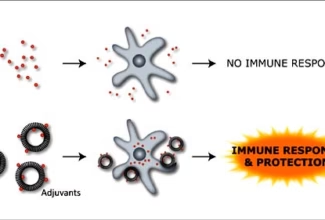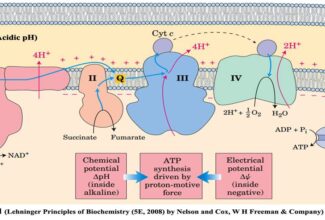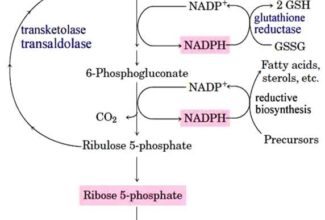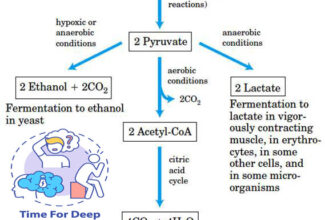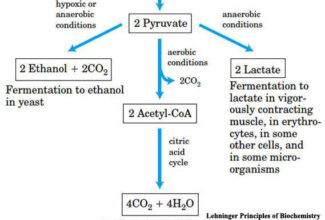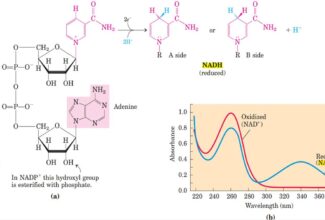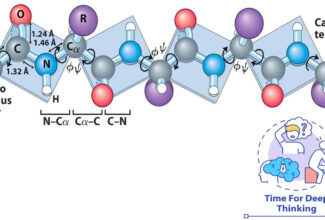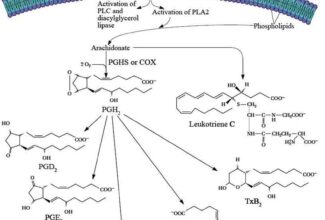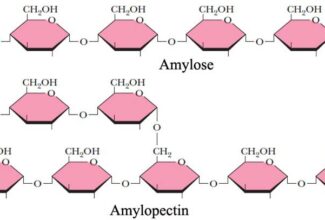
Weak Acid Base PH Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Biological Buffer Polyprotic Acid Ionic Strength
Acid and Base
As per modern concept of acid and bases developed by Bronsted, Lowry and other defines acids as proton donors and bases are proton acceptors
Each acid is therefore has a conjugate base,
Acid → Base + H+
Alkali: The term alkali is reversed for those compounds that yield OH ion dissociation
Some examples of acids and bases
Table 1 showing common acid and conjugated base
| Acid | Conjugate base |
| HCl | Cl– |
| CH3COOH | CH3COO– |
| H2CO3 | HCO3– |
| H3PO3 | H2PO3— |
| H2O | OH– |
| H3O+ | H2O |
Although it is convenient to write acid-base equilibrium as shown above, the proton does not exist as such, but is usually solvated. E.g. in aqueous media the hydrogen ion exists as the hydronium ion (H3O+)
H+ + H2O ↔ H3O+