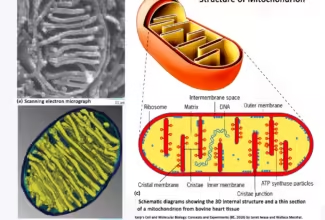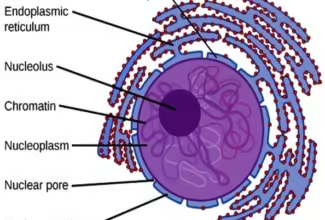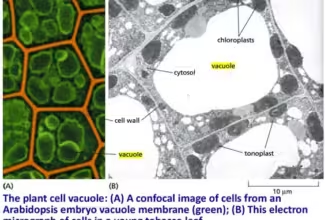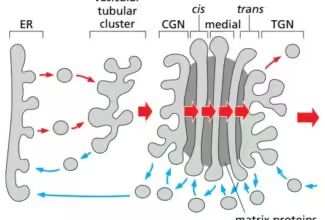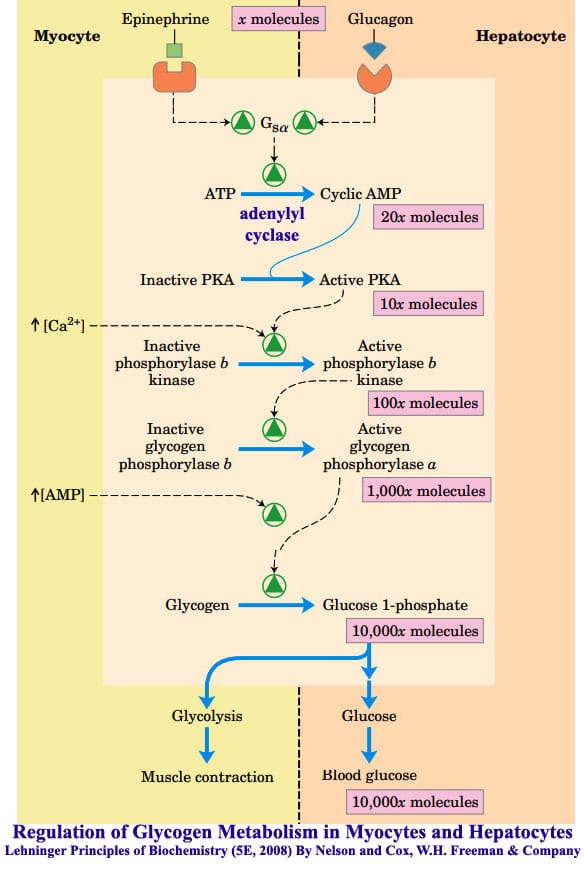
Glycogen Metabolism: Glycogenolysis and Glycogenesis and their regulation, Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism
Glycogen Metabolism: Glycogenolysis and Glycogenesis and their regulation, Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism
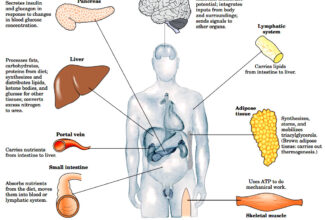
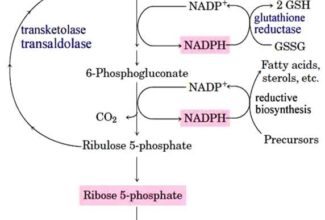
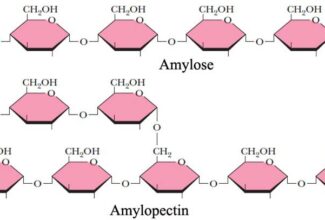
- A readily mobilized storage form of glucose.
- Highly branched structure.
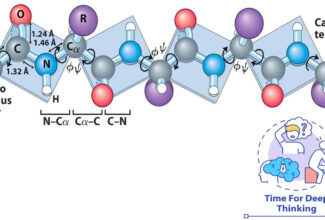
- Glucose residues linked by α-1→4 and α-1→6-glycosidic bonds linearly and at branch point at every 10th residues respectively.
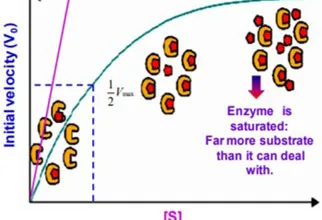
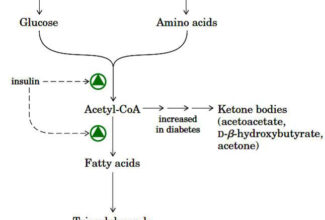
- Less energy than fatty acids then why do animals store any energy as glycogen? Why not convert all excess fuel into fatty acids?
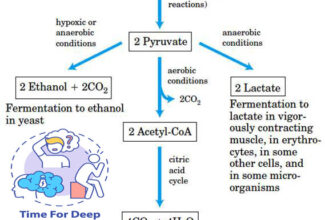
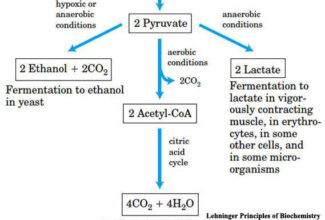
Glycogen is an important fuel reserve for several reasons.
- The breakdown of glycogen is highly controlled.
- Glycogen readily hydrolyzed to release of glucose between the meals.
- Glucose is the only fuel used by the brain, except during prolonged starvation.
- It is a good source of energy for sudden and strenuous activities in the absence of O2 unlike fatty acid.