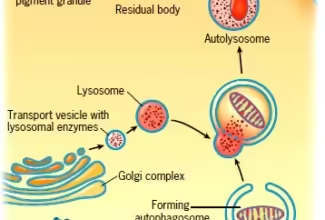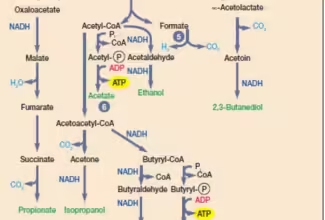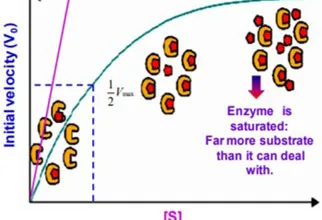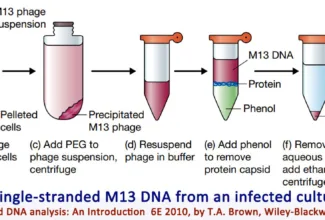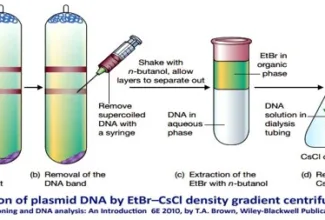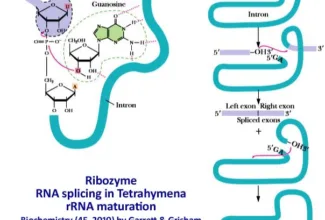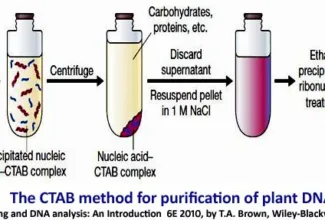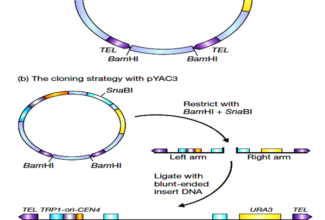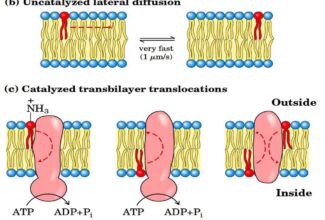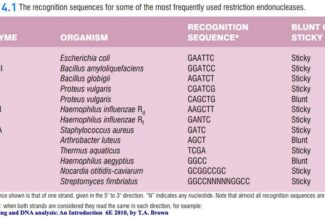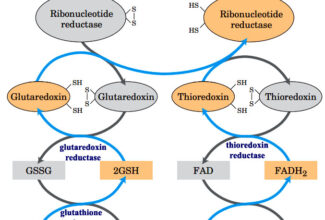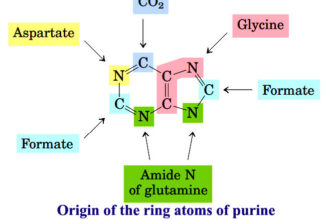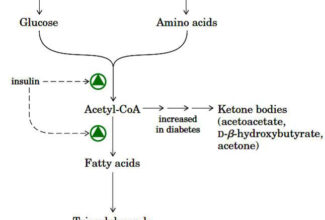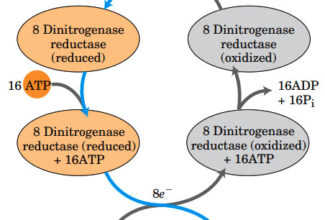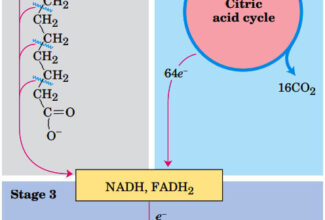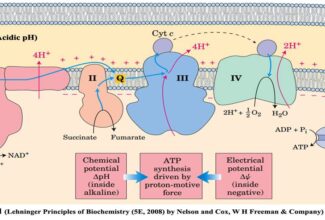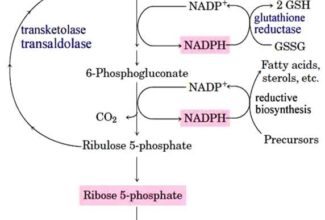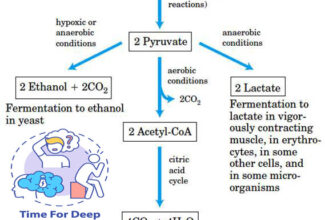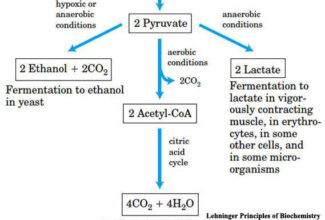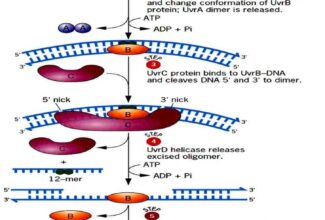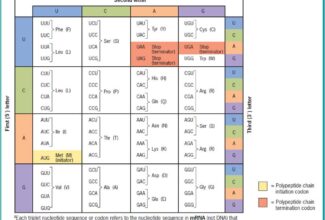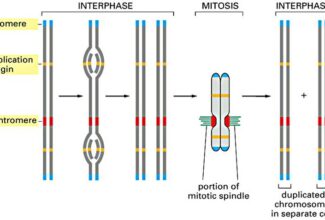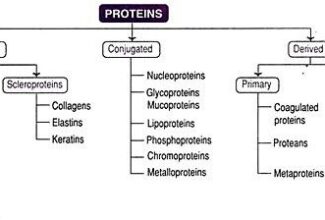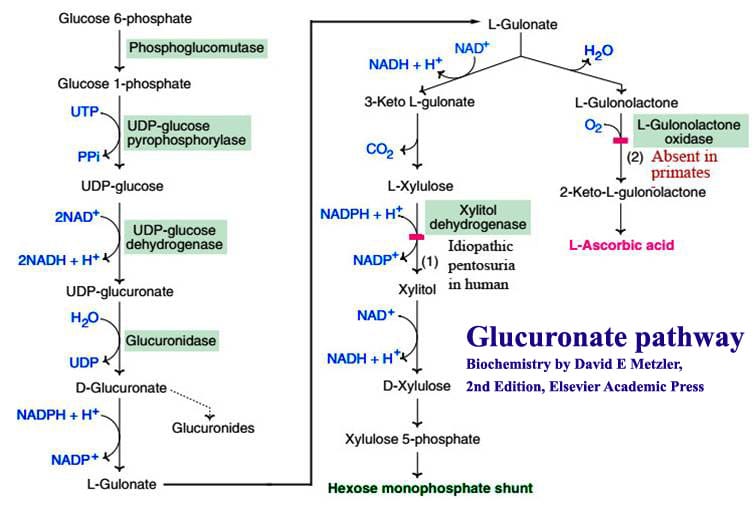
Uronic acid (Glucuronate) pathway
Uronic acid (Glucuronate) pathway
- An alternative pathway for the oxidation of glucose that do not produce ATP but used to provide activated form of glucuronate.
- This pathway is used by plants, certain animals and microorganism to produces Ascorbic Acid (blocked in primates including human).
- In human it occurs in liver
- UDP-glucuronate which is mainly used for detoxification of foreign chemicals (drugs) by increasing the solubility of drugs and for the synthesis of mucopolysaccharides such as proteoglycans and glucosaminoglycans.