Lipids Classification Nomenclature Properties and Functions
Lipids Classification Nomenclature, Properties and Functions
Fatty acids, Triacylglycerides, Waxes, Phospholipids, Plasmalogens, Sphingolipids, Cholesterol, Prostaglandins
The lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds insoluble in water and considerably soluble in organic solvents like ether, chloroform and benzene.
- As molecules that are largely hydrocarbon in nature, lipids represent highly reduced forms of carbon and, upon oxidation in metabolism, yield large amounts of energy.
- Lipids are thus the molecules of choice for metabolic energy storage.
- Hydrophobic in nature
- These are also called as lipins or lipoids which refer to “fat-like” substances that may not actually be related to the fatty acids.
- The term ‘lipid’ was first used by the German biochemist Bloor in 1943 for a major class of tissue components and foodstuffs.
Classification
- Bloor (1943) has proposed the following classification of lipids based on their chemical composition
- Simple lipids or Homolipids . These are esters of fatty acid with various alcohols.
- Fats and oils (triglycerides, triacylglycerols) (storage lipids):These are esters of fatty acids with a trihydroxy alcohol (glycerol). A fat is solid at ordinary room temperature where as an oil is liquid.
- Waxes: These are esters of fatty acids with high molecular weight monohydroxy alcohols.
- Compound lipids or Heterolipids (Structural lipids) Esters of fatty acids with alcohol and possess additional group(s).
- Phospholipids (phosphatids): consist of compounds containing fatty acids, glycerol, a phosphoric acid, nitrogen bases and or other substituent.
- Glycolipids (cerebrosides): These are the compounds of fatty acids with carbohydrates and contain nitrogen but no phosphoric acid. The glycolipids include certain structurally-related compounds comprising the groups, sphingolipid, cerebrosides and gangliosides,
- Derived lipids are the substances derived from simple and compound lipids by hydrolysis. These include fatty acids, alcohols, mono- and diglycerides, steroids, terpenes and carotenoids



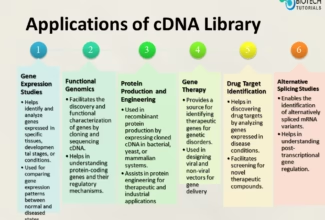
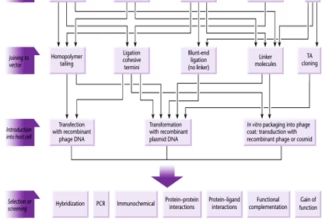
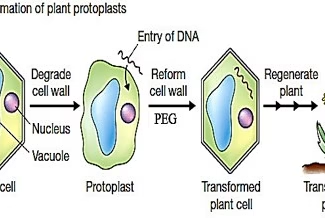
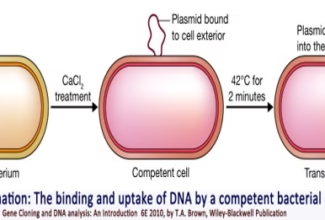







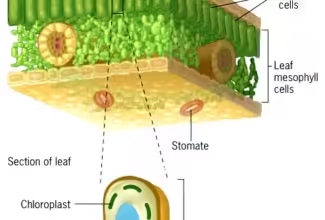
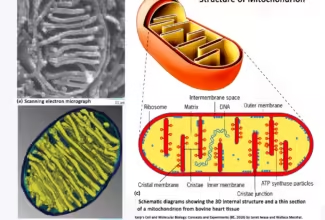
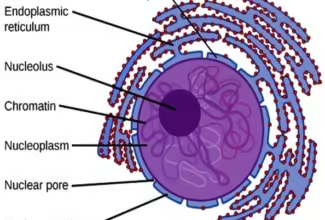
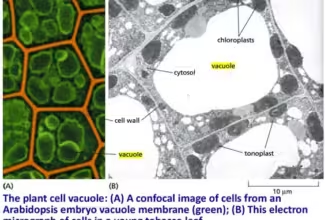
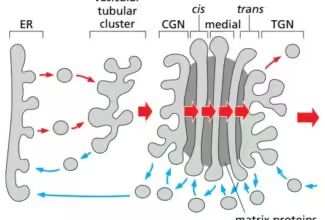
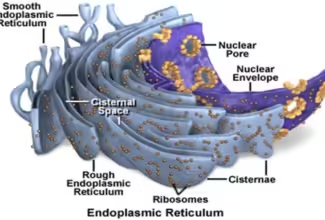
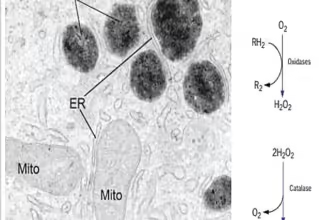
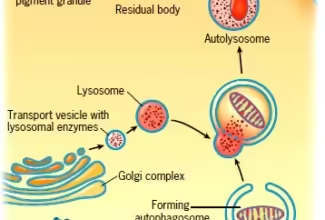

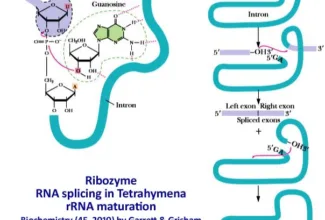
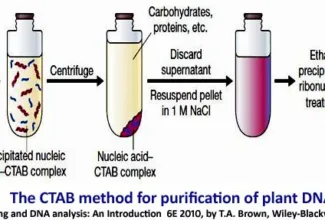
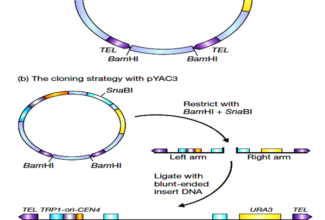


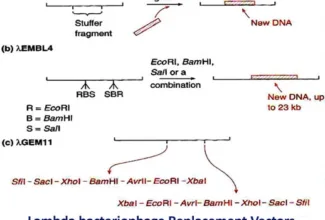








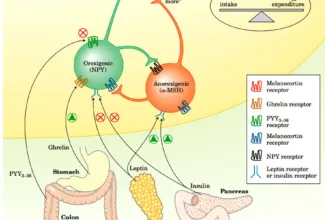

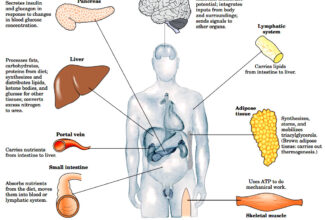




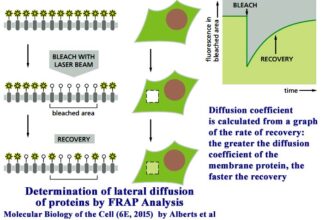
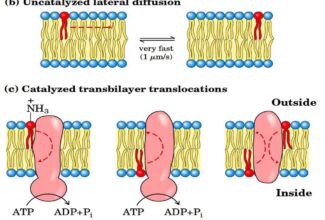





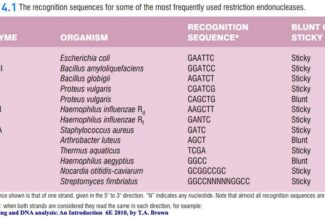
















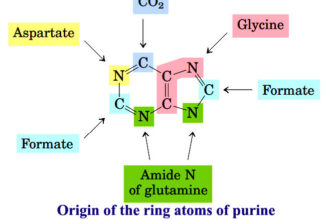












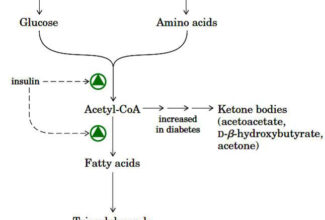

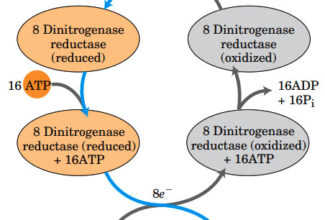






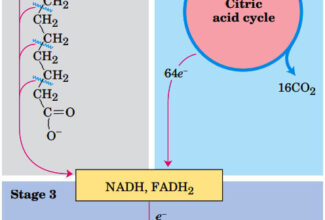









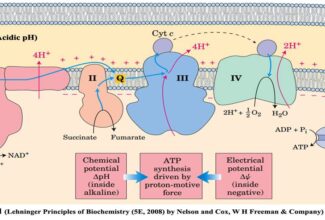

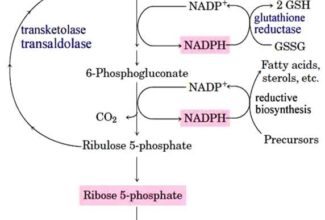






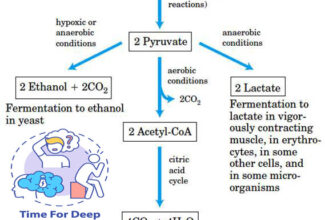
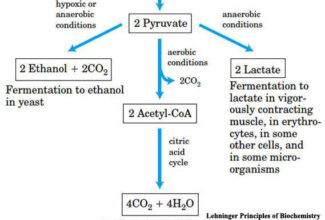

































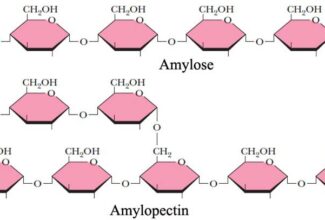



























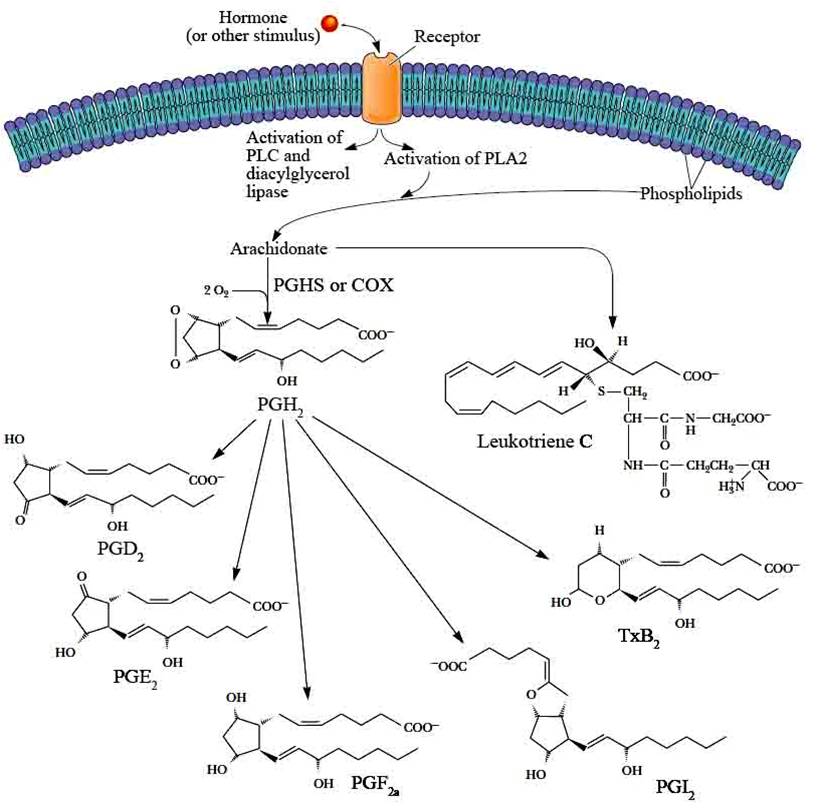
[…] Lipid structures, properties and functions […]